HRCI – международный сертификационный институт.
Преимущества сертификации HRCI:
· существует на рынке более 40 лет,
· имеет аккредитацию National Commission for Certifying Agencies (NCCA),
· выдано более 500 тысяч сертификатов по всему миру,
· сертифицируются представители более 125 стран мира,
· в 93% компаний из списка Fortune 500 работают сертифицированные специалисты,
· сертификация в 5 раз более востребована, чем другие,
· те, кто получили сертификат, имеют годовой доход на 19,712$ выше,
· доход компании выше на 25%, где работают выпускники сертификации.
Существует 3 уровня сертификации:
Рассмотрим преимущества сертификации уровня PHRi:
· работа в международных компаниях,
· уважение коллег,
· более активный карьерный рост,
· международные знания,
· возможность указывать в подписи,
· участие в конференциях в качестве спикера,
· выше востребованность на рынке,
· выше заработная плата.
Сам сертификат выдается в формате онлайн-бейджа:

Можно при желании заказать сертификат в бумажном виде. Это услуга предоставляется за дополнительную плату.

Как подготовится к сдаче экзамена на получение сертификата? Можно пройти полный курс Mike Pritula Academy..
Для вас в процессе обучения доступны:
· общение в закрытой группе,
· поддержка,
· учебные материалы для изучения и подготовки к экзамену,
· тренировочные тесты,
· ритм,
· решение возникших вопросов и сложностей.
Результат успешной сдачи экзамена для слушателей курса повышается с 78% до 98%.
На курсе подготовки к экзамену предусмотрены следующие формы работы:
Онлайн вебинар
Раз в неделю (10 недель) вы проходим онлайн вебинар, где разбираем новую тему и примеры вопросов на экзамене.
Прохождение тестов
После каждого занятия вы проходите тесты по материалам. Тесты можно проходить повторно для тренировки.
Изучение конспекта
Для каждого вебинара есть конспект лекций, который освежит ваши знания и поможет в подготовке перед экзаменом.
Регистрация на экзамен
Мы покажем, как регистрироваться на экзамен, чтобы все прошло гладко и решим проблемы, если они будут.
Экзамен в тестовых центрах сдается круглогодично. Сейчас в США и Канаде можно сдать экзамен удаленно.
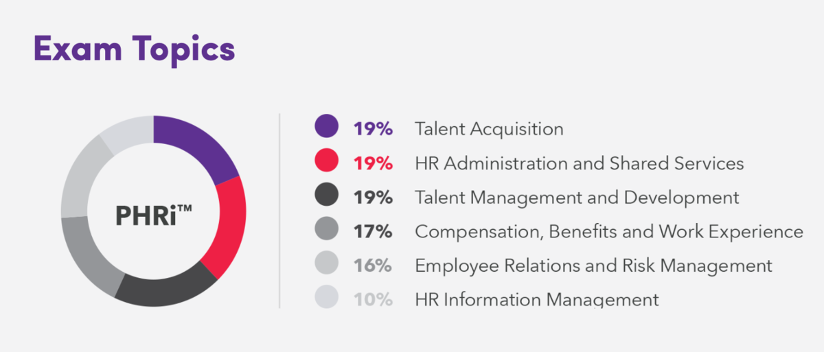
Об экзамене PHRi:
· тестовый центр Pearson VUE,
· продолжительность 3 часа и 15 минут,
· 145 оцениваемых вопросов + 25 подготовительных (не оцениваются),
· проходной балл 80%,
· язык: английский (чтение),
· онлайн за компьютером,
· стоимость: 395$ + 100$, исключения: 200$ + 100$ (список стран) + для наших слушателей из Казахстана, Украины ссылка про промокоду,
· сдача в любое время.
После прохождения курса подготовки вы будете свободно владеть следующими компетенциями:
- Рекрутинг и отбор.
- HR-администрирование и общие сервисы.
- Развитие персонала и управление талантами.
- Компенсации, льготы и опыт сотрудника.
- Отношения с сотрудниками и управление рисками.
- Информационные системы HR.
Во время обучения у вас будет личный кабинет, в котором доступны:
1. Записи каждого занятия.
2. Конспект лекций.
3. Тесты для тренировки.
Регистрация на экзамен доступна на сайте https://www.hrci.org
Подробную информацию о шагах регистрации смотри в видео:
Авторская методика в 2 раза повышает эффективность запоминания материала.
Наши результаты:
· 96% наших выпускников успешно сдают экзамен,
- показатель успешной сдачи наших выпускников в 1,5 раза выше, чем в других школах.
Первая тема курса подготовки к экзамену PHPi – Job Analysis and Design (анализ должности и дизайн работ).
Рассмотрим следующие вопросы:
1. Job Analysis.
2. Methods of Job Analysis.
3. Job Design.
Job Analysis
Схема анализа должности (модель). На каждом занятии изучаются до 5-10 подобных моделей.
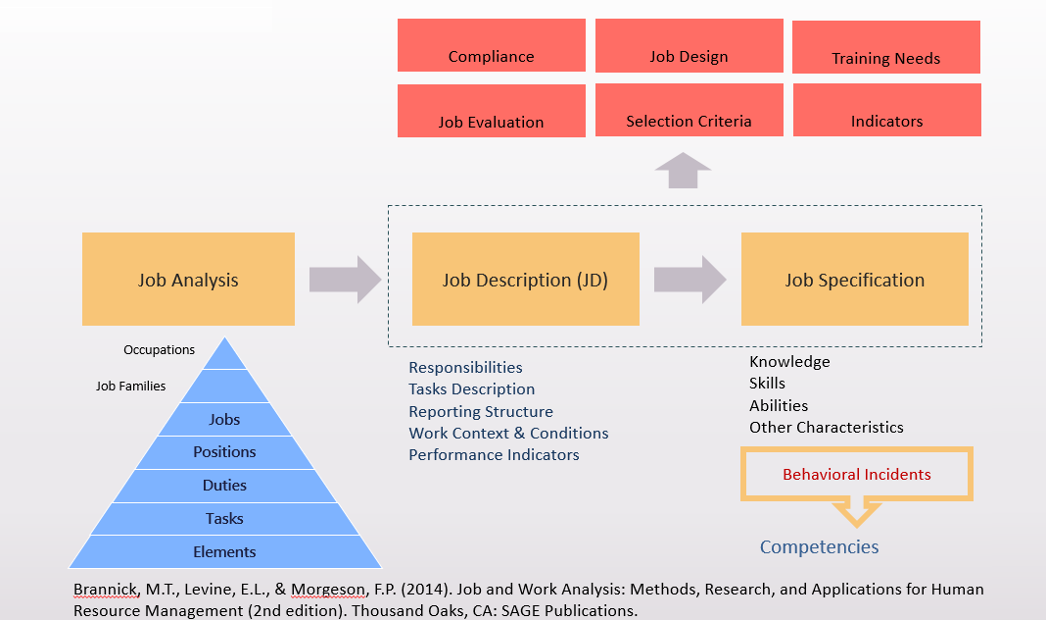
Для многих HR-функций требуется понимать, чем же занимается человек на данной должности.
Перечень функций
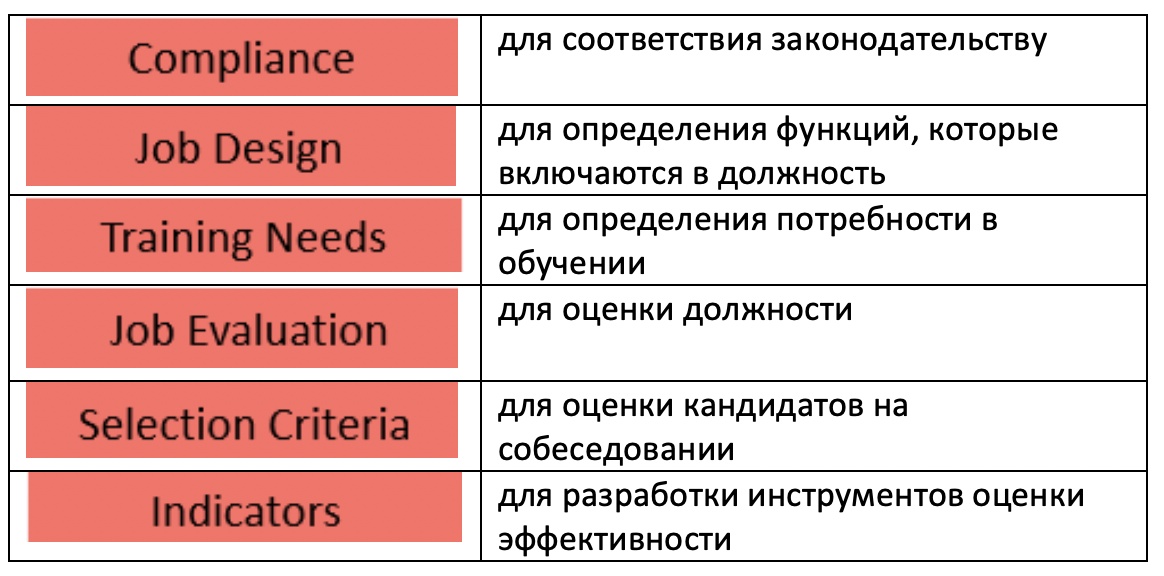
Что является результатом анализа должности?

Основные блоки описания должности
Конспект темы Job Analysis
Практически все моменты во время занятия поясняются. Как я уже сообщал, используется наша авторская методика русский + английский. При самостоятельном изучении конспекта занятия вы вспоминаете пройденное и получаете немного новой информации. Напоминаю, элементарный английский необходим.
Конспект:
· Scholars defined job analysis as ‘‘the collection of data on (a)‘job-oriented’ behavior, such as job tasks and work procedures; (b) more abstract ‘worker-oriented’ behavior, such as decision making, supervision, and information processing; (c) behaviors involved in interactions with machines, materials, and tools; (d) methods of evaluating performance, such as productivity and error rates; (e) job context, such as working conditions and type of compensation systems; and (f) personnel requirements, such as skills, physical ability, and personality traits’’ This definition of job analysis focuses on the systematic collection of data on the observable job behaviors of employees and what is accomplished by these behaviors and what technologies are required to do so.
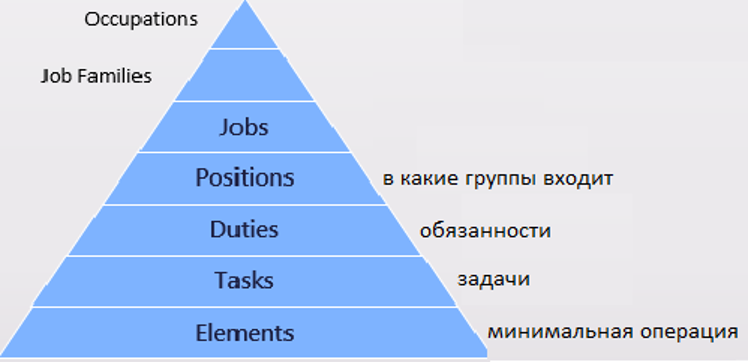
· Various authors use terms such as job, position, and task to men different things.
· Position: The duties and tasks carried out by one person. A position may exist even where no incumbent fills it; it may be an open position. There are at least as many positions in an organization as there are people.
· Job: A group of positions with the same major duties or tasks: if the positions are not identical, the similarity is great enough to justify grouping them. A job is a set of tasks within a single organization or organizational unit.
· Occupation: An occupation is a class of roughly similar jobs found in many organizations and even in different industries. Examples include attorney, computer programmer. Mechanic, and Gardener.
· Job family: A group of jobs similar in specifiable ways, such as patterns of purposes, behaviors, or worker attributes. An example of a job family might he clerical and technical,” which could include receptionists, accounting clerks, secretaries, and data entry specialists.
· Element: The smallest feasible part of an activity or broader category of behavior or work done. It might be an elemental motion, a part of a task, or a broader behavioral category; there is little consistency in meanings of this term.
· Task: A step or component in (lie performance of a duty. A task has a clear beginning and ending; it can usually be described with a brief statement consisting of an action verb and a further phrase.
· Duty: A relatively large part of the work done in a position or job. It consists of several tasks related in time, sequence, outcome, or objective. A clerical duty might be “sorting correspondence.” One task in correspondence sorting might be ‘identify letters requiring immediate response.’
· Job Description: A written report of the results of job analysis. A job description is usually narrative, sometimes given in a brief summarizing paragraph. It may he more detailed. Where job analysis was (lone by survey methods, the description may include listings of task statements found to define or characterize the job being studied, along with statistical data.
The Use of Job Analysis
· Recruitment and Selection: Job descriptions and job specifications are formed from the information gathered from a job analysis, which help management decide what sort of people to recruit and hire.
· Compensation: The estimated value and the appropriate compensation for each job, called job evaluation, which determined from the information gathered from a job analysis.
· Training and Development: Based on the job analysis, the job description should show the job’s required activities and skills.
· Performance Appraisal: Managers use job analysis to determine a job’s specific activities and performance standards.
· Job Design: Job analysis can help reveal the process of bundling tasks or units of work into a collective called a job, and/or unassigned duties. Also, job analysis can help establish groups or classes of similar jobs for compensation or performance appraisal purposes.
· Compliance: Protect the organization in the event of legal challenge. The courts in some countries have typically held that a job analysis made in good faith is admissible as evidence that the organization has attempted to validate certain of its personnel procedures and practices.
Methods of Job Analysis
Методы анализа должностей
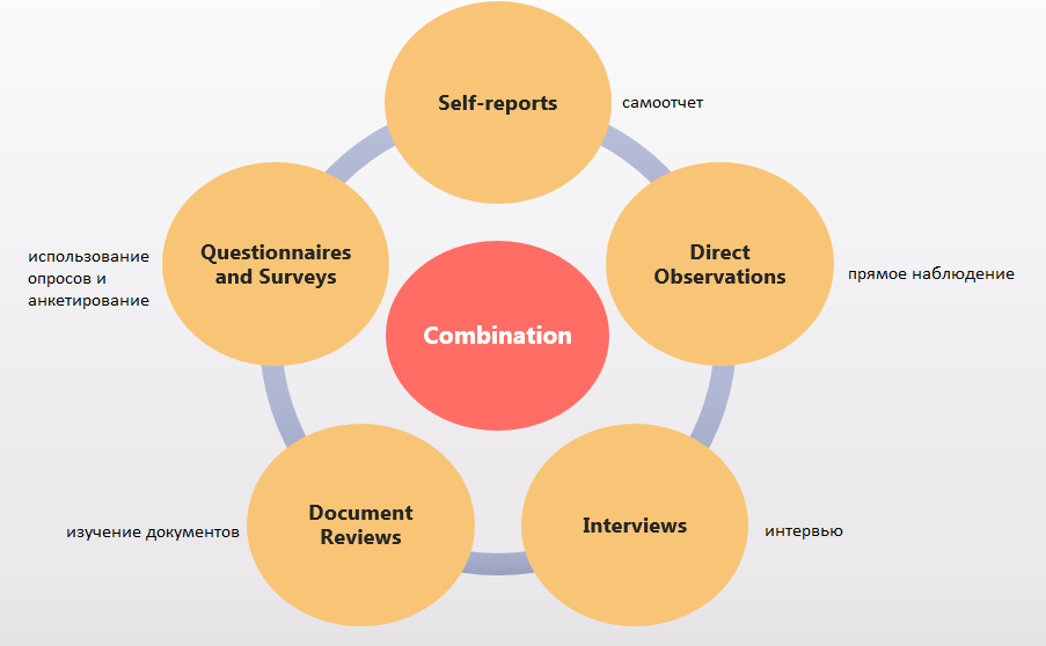
Может использоваться комбинация методов.
Конспект темы Methods of Job Analysis
• 10.1. Interview
• The three types of interviews managers use to collect job analysis data are: individual (to get the employee’s perspective on the job’s duties and responsibilities, group (when large numbers of employees perform the same job), and supervisor (to get his/her perspective on the job’s duties and responsibilities). Using an interview is simple, quick, and more comprehensive because the interviewer can unearth activities that may never appear in written form. The main problem is distortion, which may arise from the jobholder’s need to impress the perceptions of others.
• 10.2. Questionnaires
• Structured or unstructured questionnaires may be used to obtain job analysis information. Questionnaires can be a quick, efficient way of gathering information from a large number of employees. But, developing and testing a questionnaire can be expensive and time consuming.
• 10.3. Observation
• Direct observations are useful when jobs consist of mainly observable physical activity as opposed to mental activity. Reactivity can be a problem with direct observations, which is where the worker changes what he/she normally does because he/she is being watched. Managers often use direct observation and interviewing together.
• 10.4. Participant Diary/Logs
• The employee records every activity he/she engages in, in a diary or work log along with the amount of time to perform each activity to produce a complete picture of the job. Pocket dictating machines can help remind the worker to enter data at specific times, and eliminates the challenge of trying to remember at a later time what was done.
• 10.5. Quantitative Techniques
• Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ) is a questionnaire used to collect quantifiable data concerning the duties and responsibilities of various jobs, on five basic activities: 1) having decision-making/communication/social responsibilities, 2) performing skilled activities, 3) being physically active, 4) operating vehicles/equipment, and 5) processing information.
• Department of Labor Procedure (DOL) is a standardized method for rating, classifying, and comparing virtually every kind of job based on data, people, and things.
• 10.6. Internet Reference
• Standardized questionnaires are frequently distributed, with instructions, via the Internet or intranet. The danger is that important points may be missed or misunderstood, clouding results. The Department of Labor’s O*NET method can help overcome these difficulties.
• 10.7. Combination
• Of all the traditional approaches to job analysis, a combination method is probably the best because it minimizes the disadvantages and maximizes the advantages of any one approach used by itself. Of the possible combination approaches, the most common are (1) questionnaires and interviews, and (2) questionnaires, interviews, and observations.
Job Design
Модель Дизайн должности
Дизайн должности – это описание того, чем человек будет заниматься.
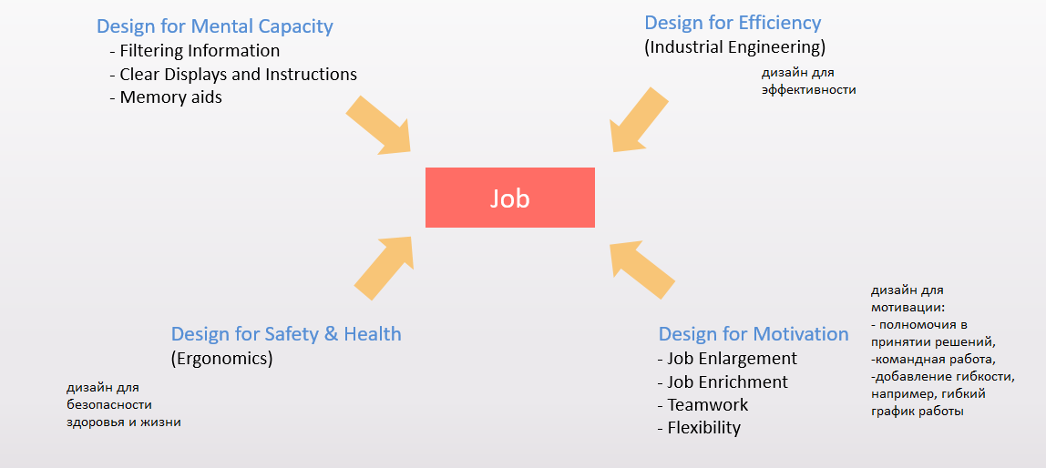
Конспект темы Job Design
• Although job analysis, as just described, is important for an understanding of existing jobs, organizations also must plan for new jobs and periodically consider whether they should revise existing jobs. When an organization is expanding, supervisors and human resource professionals must help plan for new or growing work units. When an organization is trying to improve quality or efficiency, a review of work units and processes may require a fresh look at how jobs are designed.
• Job design is the process of Work arrangement (or rearrangement) aimed at reducing or overcoming job dissatisfaction and employee alienation arising from repetitive and mechanistic tasks. Through job design, organizations try to raise productivity levels by offering non-monetary rewards such as greater satisfaction from a sense of personal achievement in meeting the increased challenge and responsibility of one's work.
• The main function of job design is to create alterations in the ways in which employees function in the workplace in order to enhance their enthusiasm for the work they perform and increase job satisfaction which in turn, increases productivity. There are 4 main approaches to the creation of job design, the first being, “design for efficiency” or “job engineering.” These terms simply refers to the expected standards of performance and the methods by which these standards are met. Technology is a major aspect of this approach; computers and all other forms of technology must be reliable and up to date and all workers must be proficient in their use and comfortable and confident in their abilities to use them.
• Design for motivation or “job enrichment” involves the designation of more duties to workers. These duties should allow employees to gain a sense of greater responsibility and accountability which in turn increases employee confidence, making tasks and duties more enjoyable so they are completed with interest and enthusiasm. Job enrichment also increases the effort of employees to work together as a team. “It is a vertical restructuring method in that it gives the employee additional authority, autonomy, and control over the way the job is accomplished” (Business Dictionary, 2010).
• Design for safety and health or ergonomics, refers to products, applications or particular tasks which are designed to lessen fatigue which may occur due to poor lighting, improperly designed work stations, excessive fluctuations in room temperature etc. It is extremely important for business leaders and managers to be aware of any of these unfavorable conditions and to correct them immediately in order to assure his or her employees are comfortable and are not being harmed during their efforts to complete tasks.
• Finally, design for mental capacity refers to the need for employers to understand the special needs of individuals who are elderly and/or those who have disabilities, either physical or mental. Special technology need to be available for individuals who may have sight or hearing problems, displays on computer monitors should be adjustable to suit the needs of those who need magnified text and special aids should be accessible to workers who have deficits in hearing. Managers need to consider carefully each employee’s physical capabilities, mental skills, organizational competence and capacity for learning before inviting an employee to take on an enriched job. Forcing more on employees than they are capable of handling will likely hurt the business and frustrate the employees.
А теперь предлагаю ответить на 3 вопроса:
1. Which of the following job analysis factors would help to establish the necessary knowledge, skills, and abilities of the Human Resource function?
a). Job context.
b). Job specifications/qualifications.
c). Performance criteria.
d). New employee orientation.
2. The PRIMARY purpose of a work log is to
a). Compute the average time needed for key tasks.
b). Identify patterns that translate into job responsibilities.
c). Determine the attitude of incumbents toward the job.
d). Help supervisors rank employees' efficiency.
3. In order to reduce information overload, orientation programs should:
a). Be modularized and spread out over a period of time.
b). Be conducted only after an employee has served on the job for a specified period of time.
c). Include a detailed employee reference manual for later use.
d). Provide continuous feedback to participants.
Легко? Сравните: 1 b, 2 b, 3 a.
Пройти подготовку к сдаче экзамена PHRi можно у нас на курсе "Подготовка к сертификации PHRi"
Получите Неограниченный доступ к 130+ курсам по управлению персоналом и бизнесу для одного человека - всего $1,000 в год!






